Selecting and implementing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is fundamentally driven by an organization’s objectives. Before an organization can identify its KPIs, it must first define its overarching objectives. Once these goals are established, management can then choose appropriate KPIs to monitor and measure the organization’s progress toward achieving them. Read on to learn all you need to know about the fundamentals of KPIs, how to choose, implement and monitor Key Performance Indicators .
What are KPIs?
KPIs, or Key Performance Indicators, are metrics that identify the aspects that contribute to project success. They assist in determining work progress and identifying areas of weakness in your process. They are an excellent technique to identify areas that may lead to failure and make necessary changes before it is too late. The key performance indicator uses quantitative data to assess the health of the initiatives.
While the scope and conditions of a company’s KPIs vary from project to project, there are certain forms of data that can benefit every firm. The top project management benchmarking metrics are Return on investment (ROI), productivity, cost performance, cycle time, customer satisfaction, schedule performance, employee satisfaction, and alignment with strategic corporate goals.
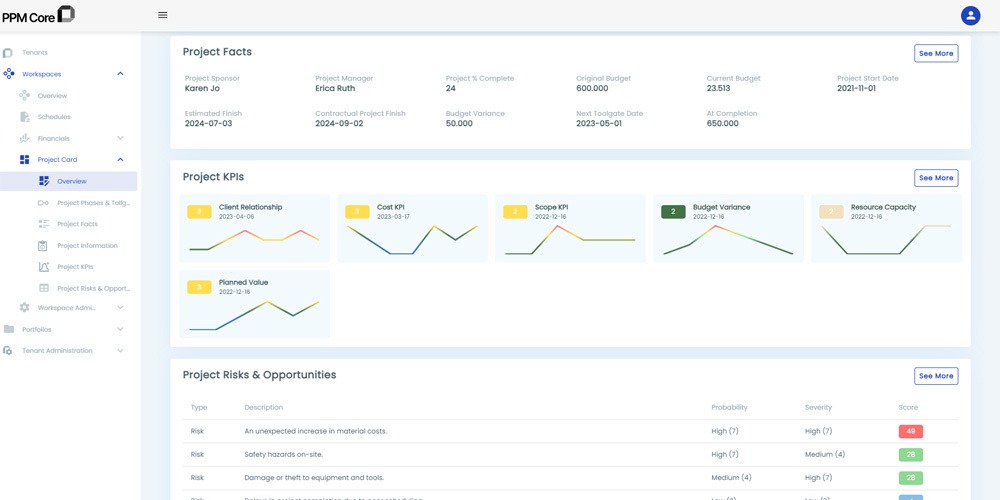
Analyze Projects Using Measurable KPIs, get a thorough understanding of the project facts, risks, and opportunities using the PPM Core Project Portfolio software
Examples of KPIs that brings value in project management are:
- Quality Metrics – Are quantitative indicators used to assess the performance, efficacy, and overall quality of a product, process, service, or system. These metrics provide objective statistics that help businesses analyze how successfully they are achieving their goals and objectives. They are crucial in many industries, serving as guidelines for informed decision-making, growth, and product delivery.
- Cost Variance– Cost Variance (CV) is an important project management statistic that calculates the difference between the estimated and actual cost of the project. Understanding and utilizing CV properly can result in more precise budgeting, efficient resource allocation, and successful project outcomes.
- Resource Utilization– It is a planning statistic that evaluates the rate at which resources are used over time and allows project managers to assess the performance of project resources effectively. Resource utilization is critical for various aspects of project management, including resource scheduling, cost analysis, and decision-making processes such as modifying the project plan, budget, or schedule. Additionally, tracking resource utilization provides visibility into a project. The more transparent and easily monitored a project is, the less likely it is to overlook critical phases. This proactive approach helps identify risks before they escalate into bigger problems that could derail the project.
- Project Health Metrics– Refers to a project’s overall functionality and progress toward completion. It includes financial success, personnel productivity, deadline compliance, budgeting, and assignment quality. To assess project health, business experts perform project health checks, which examine whether each project component meets expectations. These health checks can be performed regularly to assess project health over time or as one-time evaluations to identify issues and opportunities for improvement.
- Risk Management Metrics – A risk management process is developed to give management insight into project uncertainty. This technique is especially useful in businesses that handle several projects, and it may be used both early on and throughout the project lifecycle. It has been beneficial in detecting projects that lack an adequate risk plan. This statistic makes remarks visible and concrete to a much larger audience, resulting in rapid visibility and a strong emotional impact on managers. The fundamental part of this method is providing senior management with increased insight into the project, allowing for faster and easier project change.
Purpose of KPIs
KPIs are unquestionably useful metrics for tracking and measuring project performance. Their purpose is to provide critical information on project progress, budget, quality, and risk management, allowing project managers to make data-driven choices and take corrective action, as necessary. However, it is vital to note that KPIs are not the only measure of success; other aspects such as team collaboration, creativity, and innovation are equally significant and beneficial.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) in project management provide numerous benefits. According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), aligning KPIs with broader organizational strategy enhances visibility and communication of project impacts, thus driving better decision-making and project success.
The benefits of using KPIs are various. They assist in monitoring progress, identifying areas for improvement, making informed decisions, measuring the impact of actions, and ensuring that everyone is on the same page. By providing a clear and objective view of the project’s status, KPIs enable steering projects towards success and achieving the best possible results. Therefore, while KPIs are essential, they should be complemented by fostering a collaborative and innovative team environment to truly excel in project management.
Aligning KPIs with Objectives
The objectives in project management serve as a roadmap for the project team, enabling them to work toward specific, well-defined goals. Therefore, a clear set of project objectives can help manage expectations, guide the decision-making process, and provide a basis for monitoring and controlling the project throughout its life cycle.
In order to know how to choose and implement the right key performance indicators, companies must have a clear vision of what they hope to achieve and why. Their strategy and objectives should be aligned with purpose, vision, and values, and reflect the competitive advantage and customer needs. Utilization of frameworks like SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) or OKR (Objectives and Key Results) help companies to plan and measure strategy and objectives.
Criteria for Selecting KPIs
Once the identification process is established and the goals and objectives are defined, it is critical that businesses choose the appropriate measurements. The four principles listed below can serve as the foundation for a company’s strategic management approach, promoting performance improvement at all levels of the organization.
Relevance
A KPI is the measurable expression of achieving a targeted level of results in an area relevant to the organization. It could be the achievement of a strategic goal or an aspect that is critical for decision-making. To maintain a solid connection, KPIs must adjust as their strategic goals change.
Feasibility of measurement
The feasibility of measuring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) refers to the practicality and effectiveness of tracking specific metrics to evaluate an organization’s success in achieving its objectives. It involves assessing whether the chosen KPIs can be accurately measured, monitored, and used to provide actionable insights. Factors influencing feasibility include data availability, measurement tools, and the relevance of KPIs to organizational goals.
Data availability
Data Availability assesses the overall efficacy and efficiency of data operations within an organization. Most organizations struggle to transport data from point to point while also providing relevant insights to teams and business leaders. Companies are currently dealing with inadequate insight into their data sources, insufficient data pipelines, and low data quality.
By providing a centralized management of data, meaning one platform where all the data is stored and shared between teams, companies can plan, analyze, and prioritize data with ease and make informed project decisions.
Ease of understanding and communication
Effective understanding and communication are the foundation of a high-performance team. It ensures that information is passed on in a timely and correct manner, minimizes misunderstandings, and contributes to a cohesive and effective work environment. When team members communicate successfully, they may coordinate their efforts, collaborate effectively, and work toward shared objectives.
It contributes significantly to a team’s success in a variety of ways, including:
- Project Management – In project management, KPIs are used to assess the efficiency of performance. For accuracy, realistic process reflection, and success in meeting the objective. KPIs can reliably, consistently, and precisely track the impact of an adjustment and provide a clear vision of the project’s trajectory.
- Problem Resolution – KPIs play a critical role in problem resolution within project management by providing measurable values that help project managers and teams understand how effectively they are achieving key business objectives.
- Decision Making – KPIs provide data-driven insights, enabling project managers to make informed decisions about where to allocate resources, which tasks to prioritize, and which strategies to implement for problem resolution.
Implementing KPIs, Monitoring and Reporting
How to Choose and Implement Key Performance Indicators Data is an essential component of an effective project management process because it enables project managers to track progress toward project goals and objectives, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions. The following steps can increase the project’s efficacy and impact.
- Data collection: – Gather information on each KPI using appropriate data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, or observations. The procedure for collecting data should be standardized and systematic to ensure that the information is accurate, valid, and useful.
- Data analysis:– Apply relevant statistical procedures to the data, such as descriptive statistics, regression analysis, or hypothesis testing. Use data visualization techniques like graphs, charts, or maps to convey data in a clear and succinct manner.
- Monitoring and Reporting:– Interpret the outcomes of the data analysis and report on progress toward the KPI targets, emphasizing areas of success and areas for improvement. Use the findings to inform decisions and improve project performance. Monitor performance and compare the progress with the planned data.
- Feedback and Learning:– Share the data analysis findings with project stakeholders, including project staff, beneficiaries, and partners, and solicit feedback and suggestions. Use the input to improve the data collection and analysis process while also learning from the findings.
Conclusion
The process of knowing how to choose and implement the right key performance indicators is crucial for any organization aiming for sustained success. By aligning KPIs with strategic goals, understanding the purpose, setting the criteria for selecting, and regularly monitoring performance, companies can ensure they remain on track to achieve their objectives. Sticking to the best practices like focusing on quality, ensuring relevance, and using real-time data will further improve the effectiveness of KPIs. Well-chosen and well-implemented KPIs enable companies to make informed decisions, drive continuous improvement, and maintain a competitive edge in the project management landscape.
PPM Core Cloud Software can play a vital role in selecting the right KPIs for project portfolio management.
It provides centralized management for projects and portfolios, providing a simple way to monitor the performance of each project and compare progress versus planned data.
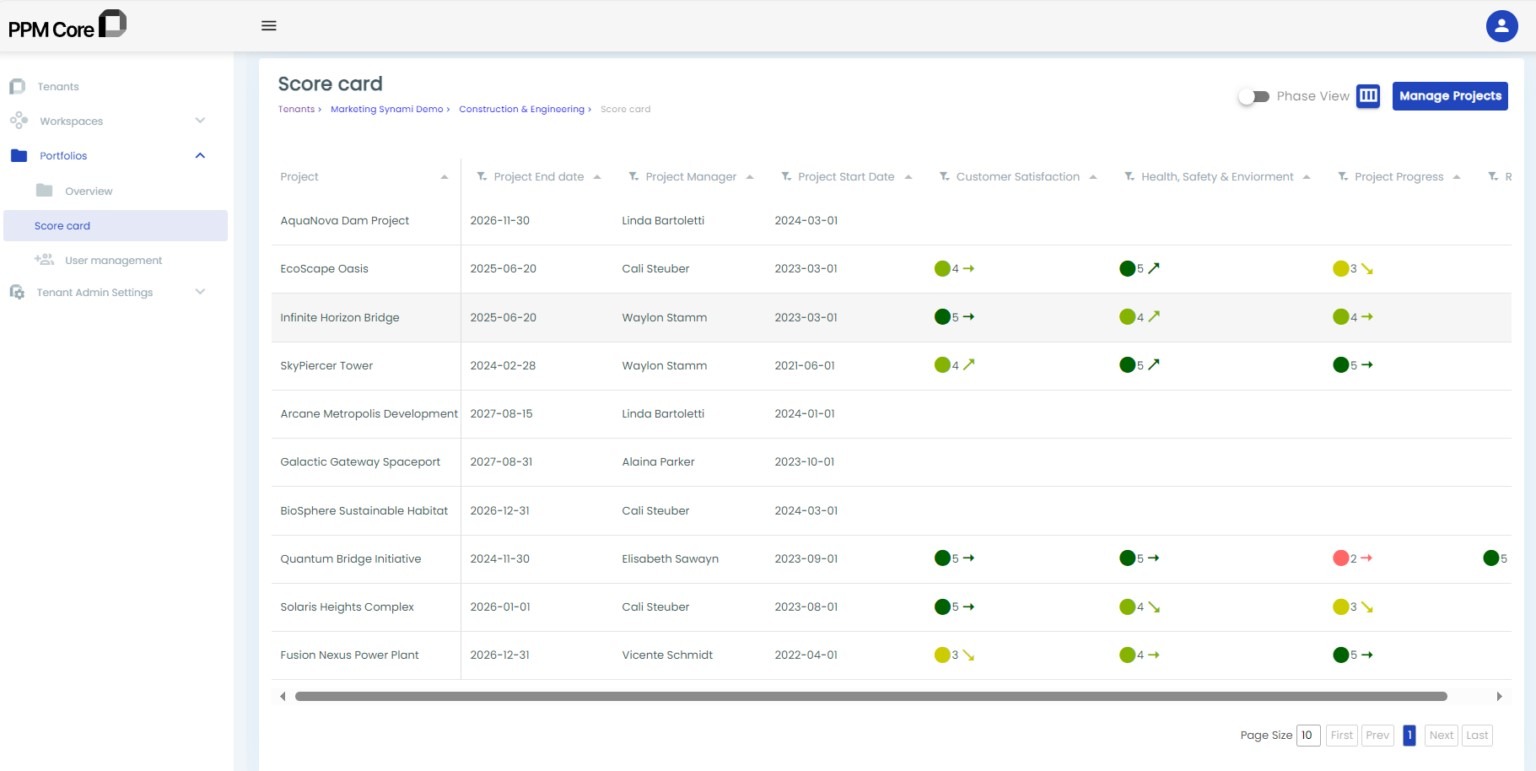
Users can organize, analyze, and prioritize projects using the Project Score card in PPM Core
The Portfolio Management Feature provides the option to analyze projects using measurable KPIs and the organization and prioritization of projects. By managing all aspects of the projects, implementing management objectives, facilitating easy navigation through project data, and obtaining key insights for project and portfolio reporting, project managers can make informed decisions and effectively guide organizations toward achieving their goals and objectives.
Book a free demo an learn all about PPM Core and its features

