Cost Module: Manage Project Finances with Precision
Project Cost Management
Overview of the importance of cost management and cost module in projects
Project Cost Management is one of the important disciplines of project management that includes the cost planning, controlling, and analysis of project cost. It helps to achieve project goals in terms of cost anywhere near the intended budget, alongside quality and the scope of the project. It is one of the key prerequisites for successful project activities since its effective management is closely related to revenue and efficiency (Smith., 2014).
Some of the common project cost management activities include; cost estimating, actual cost monitoring cost budgeting, and cost control throughout the project. The management of cost is crucial in projects since it involves the effective control of cash and management of expenditures for a project to avoid exceeding the recommended financial limit on the project (Rehman et al., 2013). These activities are necessary to prevent additional costs for the project and to correctly allocate resources. When funds for each project will not exceed the planned levels any changes will be costly to implement besides satisfying the stakeholders on the result of the project. This also benefits the profitability and sustainability of projects since necessary caveats are put in place to measure up to optimum organizational goals and objectives within budget limits (Al-Nady et al., 2016).
Centralized Financial Control in Projects
Single source of truth for Project Managers
Cost management offers the Project Managers a single financial tool where all financial aspects of the project can be managed efficiently. It enables project managers to combine all financial segments of the project and track the costs in real time (Smith., 2014). Project cost control involves the collection of cost data within an organized central point that can allow the Project Managers to monitor the expenditures, plan on resources, and offer timely and proper statements of account to other stakeholders. It also helps to make sure that various decisions made on the project are right and keep the project within budget for better profitability (Mansor et al., 2016).
Benefits:
This provides several benefits from implementing the Cost Module
- Real-Time Tracking of Costs: This helps the project managers monitor the expenses when they happen or anything beyond the excess spending.
- Budget Control: Financial data must be updated more frequently than other data, allowing teams to modify the cost estimates to meet a project’s new requirements if they occur.
- Financial Transparency: When the money is kept under central operations, there is always an audit trail and this enhances or implies controlled transparency.
A well-managed cost module supports these processes by enabling the Project Managers to assess and determine at what point in the project the cost has deviated from the budget so that corrective action can be taken where required. This reduces unfavorable outcomes in the financial aspects of the project and enables the stakeholders to work on the financial reports accurately and credible (Mansor et al., 2016).
Driving Financial Precision and Accountability for Project Success
Process of collaboration between Project Managers and Cost Controllers
The relationship between the Project Manager and Cost Controller has to be effective to ensure the project has strong financial probity. The roles of Project Managers and Cost Controllers are to exchange the necessary financial information to make proper decisions about resource availability, as well as the budgeting and cost control mechanisms (Malagueño et al., 2021). Project Managers are mainly responsible for ensuring the project activities are in line with the budget or financial plan of the project, while Cost Controllers deal with generating elaborate financial reports and planning. Together, they ensure that costs are kept low and that the overall profit on projects is optimized through unintended control of financial plans (Crawford et al., 2004).
Insights from the model’s project data
Key outcomes of this collaboration include:
- Optimized Resource Allocation: When analyzing real-time data, Project Managers are better placed to assign appropriate labor, materials, and time to different phases in the project.
- Cost Minimization: Through the indication of regions whereby expenses may be cut while affecting quality negatively, Project Managers and Cost Controllers can guarantee that the project is profitable.
- Improved Profitability: To improve the overall profitability of a particular project, they need to ensure they analyze detailed financial information and also arrive at proper decisions that must result from such information.
This makes it possible to improve on the financial details that are needed in the provision of complex tasks in which there are several parties or complicated supply systems. It also establishes accountability of costs, whereby every member of the team knows what it costs to do something (Crawford et al., 2004).
Main Challenges of Implementing Project Cost Module in Projects
There are several difficulties related to the implementation of cost module which include (Smith., 2014):
- Resource Allocation Issues: This means that being able to ensure resources are being used where they are needed the most continues to be a problem, especially in cases where there are working on dynamic projects or those that require a short time for their completion.
- Inaccurate Estimates: A primary problem of project cost control is that cost estimates are commonly derived from assumptions or otherwise limited information.
- Outdated Tools: Most organizations still employ traditional or rudimentary means of controlling project costs, that contain inadequate control procedures for cost tracking.
Automating Financial Workflows to Improve Project Cost Accuracy and Efficiency

Do you find this article interesting?
Subscribe to our Newsletter for updates on the latest blog articles.
Digital software in operations provides for efficient management of large projects through efficient allocation of finances by automating the processing of financial aspects of the work, improved costing of the projects, and frequent real-time updates for work progress. These tools automate the planning and tracking of financial resources and expenses, thus helping Project Managers work more effectively and get better results for projects and their organizations’ bottom line (Matveeva et al., 2021).
Conclusion:
The addition of a cost module into Project Management processes improves its financial accountability and guarantees project effectiveness. They help Project Managers ensure that all financial data related to a particular project are brought together into a single system to provide up-to-date data for use in decision-making. Managers of the project and cost controllers work together to improve the usage of resources and reduce costs thus enhancing the profitability of the project. There are significant difficulties in the implementation of cost management systems, but thanks to modern technology, optimal tools are available to bring projects to fruition and on schedule cost-efficiently.
One of those tools that can help teams and organizations in optimizing control and controlling the costs effectively is PPM Core.
With a focus on efficiency, PPM’s Core Cost Management feature streamlines financial transactions, improves budget precision, strengthens financial control, and ensures projects stay within budget.
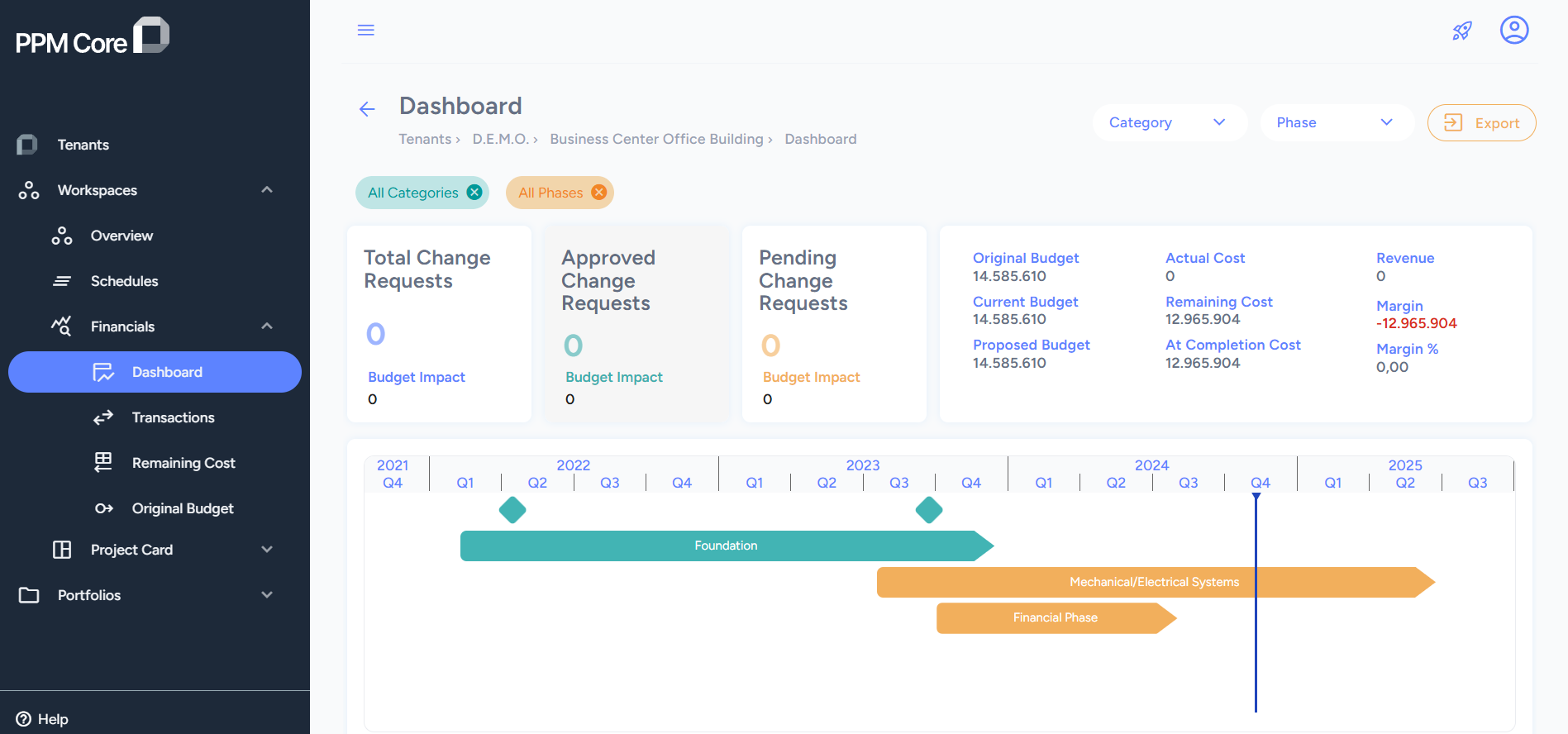
Overview of the financial dashboard in the PPM Core Cost Management Feature
References
Al-Nady, B. A. H. A., Al-Hawary, S. I. S., & Alolayyan, M. N. (2016). The role of time, communication, and cost management on project management success: An empirical study on a sample of construction projects customers in Makkah City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Services and Operations Management, 23(1), 76-112.
Crawford, J. K., Cabanis-Brewin, J., Bigelow, D., James, C., & Pennypacker, S. (2004). Project Management Roles and Responsibilities. Center for Business Practices, Havertown PA, USA.
Malagueño, R., Gomez-Conde, J., de Harlez, Y., & Hoffmann, O. (2021). Controller involvement in a project management setting: effects on project functions and performance. Journal of Applied Accounting Research, 22(2), 334-364.
Mansor, Z., Arshad, N. H., Yahya, S., & Razali, R. (2016). The competency of project managers in managing agile cost management. Advanced Science Letters, 22(8), 1930-1934.
Matveeva, N. S., Lebedeva, J. A., & Petrina, O. A. (2021). Application of digital technologies in public finance. In Socio-economic Systems: Paradigms for the Future (pp. 577-585). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Rahman, I. A., Memon, A. H., & Karim, A. T. A. (2013). Relationship between factors of construction resources affecting project cost. Modern Applied Science, 7(1), 67-75.
Smith, P. (2014). BIM & the 5D project cost manager. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 119, 475-484.
Smith, P. (2014). Project cost management–Global issues and challenges. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 119, 485-494.